Bonjour is a type of zero-configuration networking protocol that was developed by Apple, to enable auto discovery of devices and services on a local network. For devices and services to be discoverable by each other, they must be connected to the same network segment/same VLAN. Bonjour uses mDNS, which is DNS-form of queries that are sent by the devices on the network using a multicast IP address. The devices on the network that receive this packet will respond back with a list of services they offer.
For example, instead of manually setting up a printer on a laptop, the laptop can discover devices offering printing services on its local network. The only requirement here is that the devices and services need to reside on the same network segment. By default, the mDNS packets are limited within the L2 boundary.
How to enable Bonjour/mDNS
By default, when a WLAN is created, mDNS packets are allowed and not blocked. In a single/flat VLAN configuration, the devices can discover other devices/services. This means, if a laptop and a wireless printer are both on VLAN 100, the laptop can discover the printer. A laptop connected wirelessly can also discover a wired printer on VLAN 100.
We recommend enabling the wireless filter on the WLAN setting as shown below. When the filters are enabled, mDNS packets are dropped and not transmitted back on air which will disable the discovery process for wireless devices/services. Enabling the filters will not block discovery of wired services on the same VLAN. To allow wireless discovery, enable the mDNS knob in the configuration.
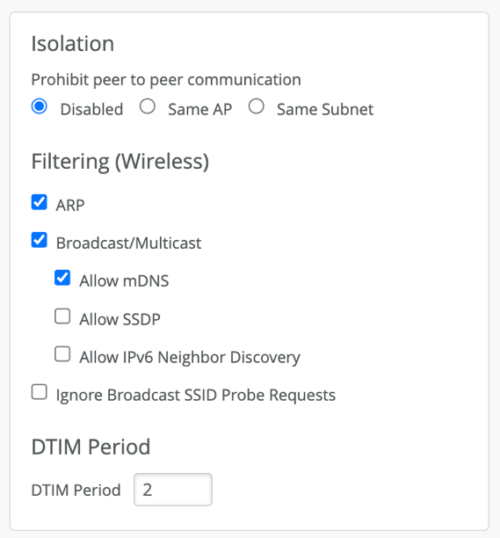
In an enterprise network, devices connected on a same WLAN are often found on different VLANs by using a VLAN pool, dynamic VLAN etc. Auto device/service discovery will not work across VLANs. To enable the auto discovery across VLANs, bonjour gateway needs to be configured in the WLAN configuration. Bonjour Gateway configuration is covered below.
mDNS is an extremely chatty protocol and turning on the bonjour services without understanding the types of devices connecting to the network can cause undesirable network issues. It can lead to capacity issues at the least and at worst can cause a multicast flood impairing the wireless/wired network.
Follow the best practices and allow only what the business demands.
Bonjour Gateway
Bonjour Gateway solution on Mist APs provide assisted bonjour service discovery for users residing on multiple VLANs on an enterprise network. The traditional bonjour/mDNS services are bound to a L2 boundary, wherein the service discovery works only when clients and the services reside in the same L2 network. Enabling bonjour gateway on the APs will allow clients to discover services residing on different L2 networks.
Mist Bonjour Gateway is a hybrid stateful/stateless solution that leverages service caching to provide quick and filtered responses, at the same time relying solely on user-initiated mDNS queries to build up the cache, instead of actively building the cache to optimize overhead and make sure that discovered services are up to date.
Mist Bonjour Gateway runs on every AP serving a WLAN in a coordinated fashion. In addition, all Bonjour/mDNS responses are converted to unicast to make sure filtering rules can apply, and wireless airtime utilization is optimized.
Discovery of services can be restricted to role and location-based control on a per-service basis. A role restricted example, a wireless user with a user-role “teacher” can discover and cast screen for Airplay service in a classroom but wireless-users with user-role student will not be able to discover these services. A location-based example is when users can discover printers only the same floor as the AP they are connected to.
This document mostly discusses about bonjour gateway configuration for locally bridged WLANs. The same configuration applies to WLANs being tunneled through Mist Edges. Please refer to the section for Mist Edge to understand how to enable Bonjour Gateway for tunneled WLANs. We also discuss recommendations and best practices to avoid excessive overhead of mDNS flooding in your network that can potentially lead to issues.
Configuration for Bonjour Gateway
Bonjour Gateway can be enabled per WLAN under the WLAN settings. This can be done through WLAN Templates or Site > WLAN. Select the WLAN you need to configure the WLAN settings. Scroll to the bottom of the “Edit WLAN” popup to see the “Bonjour Gateway” configuration as shown below.
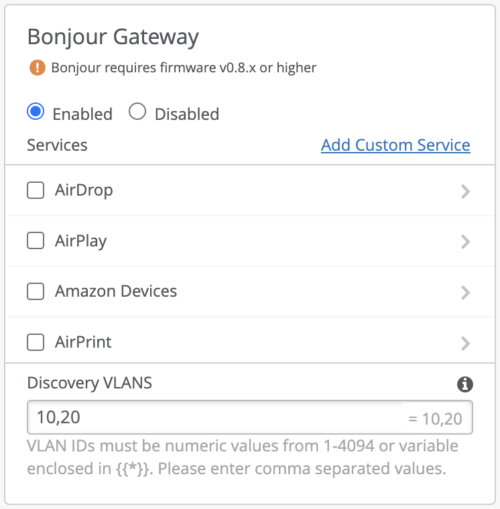
Bonjour Gateway is disabled by default, which means no Bonjour Services will be allowed through a gateway. Service/Services must be explicitly selected to permit service to be discovered by a user. Note that if Bonjour Gateway is enabled on the WLAN, Mist AP would automatically enable Broadcast/Multicast filter and drop any unsolicited mDNS traffic going in direct to the wireless clients.
Bonjour Devices Discovery
Once enabled, we need to configure all the VLANs on which services can be discovered. VLAN ID(s) or Site Variables need to be provided for the services to be discovered. The bonjour devices can reside on wired or wireless network.
By default, Bonjour Gateway will not discover any devices if the Discovery VLAN is not configured. For example, if a WLAN has users/devices in VLANs 10, 20, 30 that need to discover each other we need to specify all the VLANs under the discovery VLANs. For any additional VLAN that is not part of the WLAN config (for example a wired VLAN), use Discovery VLAN field to allow Bonjour Gateway to learn devices from that VLAN. Note that Discovery VLAN should be allowed at the AP switchport.
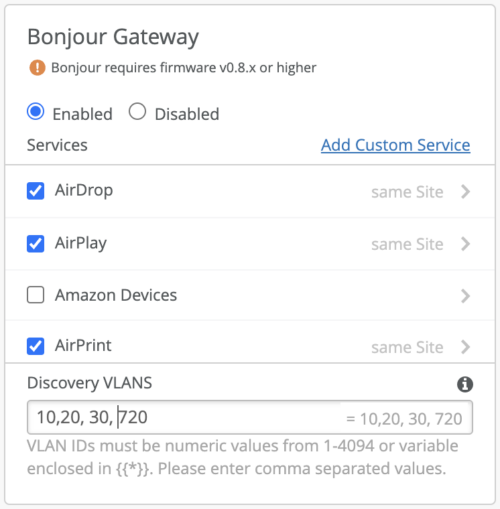
In the image below, VLANs 10, 20, 30 are part of the WLAN and VLAN 720 is enabled for wired bonjour device discovery. APs will send forward the service discovery query from a wireless clients coming from over the air on all the Discovery VLANs. The responses from the bonjour devices from all the discovery VLANs are forwarded to the client (unicast) and are added to the cache as well on the AP.
Access Control for Bonjour discovery
Discovery of Bonjour services can be restricted to a user-role or location of the user. Each Bonjour service can be configured for discovery based on location and role. Let’s look at both the rules and options.
Proximity -Based discovery
Location based rules allow a user to discover only services that are in close proximity to a user, like printers on the same floor and so on.
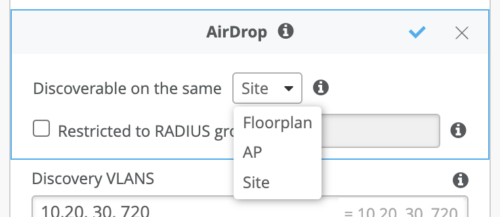
- Discoverable on the Same Site (both a user requesting a service and bonjour device needs to be connected to the AP that belong to the same Site). This is the default setting.
- Discoverable on the Same Floorplan (both a user and a bonjour device need to be connected to the AP that are placed on the same Map under Live View).
- Discoverable on the Same AP (both a user and a bonjour device need to be connected to the same Access Point)
Notes: Floorplan and AP options would need careful RF design to achieve best results. Location-Based filters are only applicable to bonjour devices connected via WiFi. For wired-only bonjour devices this setting will be ignored.
User Role-Based rules
Role Based restrictions allow you to limit bonjour service discovery to a specific user role within the same SSID, for example teacher vs students on an 802.1X WLAN or employee vs guest for printer discovery.
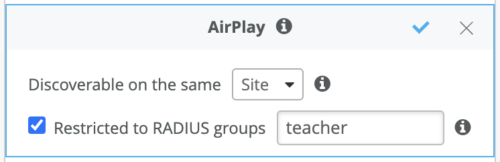
Notes- Role based bonjour discovery filter is achieved by mapping a client to a user role via AAA Attribute received from a RADIUS server as part of the 802.1X or a MAC Authentication. We can user Filter-Id, aruba-user-role or Airespace-ACL-Name AVPs inside Access-Accept. Multiple roles can be configured per service (comma-separated). A label must be created with type AAA Attribute to enable this feature. Labels can be created by navigating to Organization > Wireless > Labels.
Custom Bonjour Services
Mist provides a set of pre-defined well-known Bonjour Services (like AirPrint, AirPlay, GoogleCast etc), while allowing for flexibility in defining custom service rules. All bonjour/mDNS services follow specific syntax to define service name, such as airplay._tcp._local. In mist custom service can be defined as wildcard, for example a service such as homeconnect._tcp._local can be enabled just by adding homeconnect as a service name:

Bonjour Gateway on Mist Edge
Mist Edge, by default, does not allow bridging of BCMC traffic across AP tunnels, hence any mDNS request received through the AP tunnel will not be forwarded to other AP tunnels. This is the default behavior in place to avoid forwarding chatty protocols like mDNS, SSDP to be flooded on all the AP tunnels if bonjour services are not required. Wireless clients can discover wired services that can be discovered upstream of Mist Edge.
Bonjour service discovery across wireless users/devices can be enabled for tunneled WLAN by configuring the Mist Edge to forward mDNS traffic to all tunnels or only tunnels that are originating from the same site, giving additional level of flexibility and scale when it comes to Bonjour deployments. This option is not exposed on the UI as of today and needs configuration on the backend. Please contact Juniper-Mist for more information on configuring bonjour gateway for tunneled WLANs.
Bonjour Pre-Requisites
- AP firmware should be version 0.8x or higher.
- The user and the bonjour service should have L3 connectivity.
- List of bonjour services that need to be enabled.
- How and who will be able to discover services.
- If proximity or location based bonjour discovery is used, a solid RF design should be considered.
Bonjour Best Practices
Any plug-n-play device and protocol discovery (mDNS) can be very chatty and the large scale of wireless devices and users discovering services can hurt network performance or even quickly bring down networks. Defining a flood boundary is very important while enabling bonjour gateway in your deployments to limit the mDNS floods when a large number of wireless users are connected to the network and are trying to discover services.
These steps can help limit the packet overhead in the network –
- Pooling bonjour devices in a few dedicated discovery VLANs.
- Using proximity and role-based discovery policies to limit discovery of bonjour devices.
- When enabling custom bonjour applications, we recommend enabling the service in a limited capacity before the application behavior is vetted and ready to production.
Troubleshooting Bonjour
In the event the client is unable to discover the bonjour devices on the network, packet captures can be initiated from the admin UI to check if AP is receiving the mDNS query packet OTA and check if the AP is forwarding this on all the discovery VLANs (wired and wireless).
Packet Captures can be done by navigating to Site > Wireless > Packet Capture. Packet captures can be done for specific clients, AP uplink or specific WLANs. We can use the advance filters to filter on UDP port 5353.


